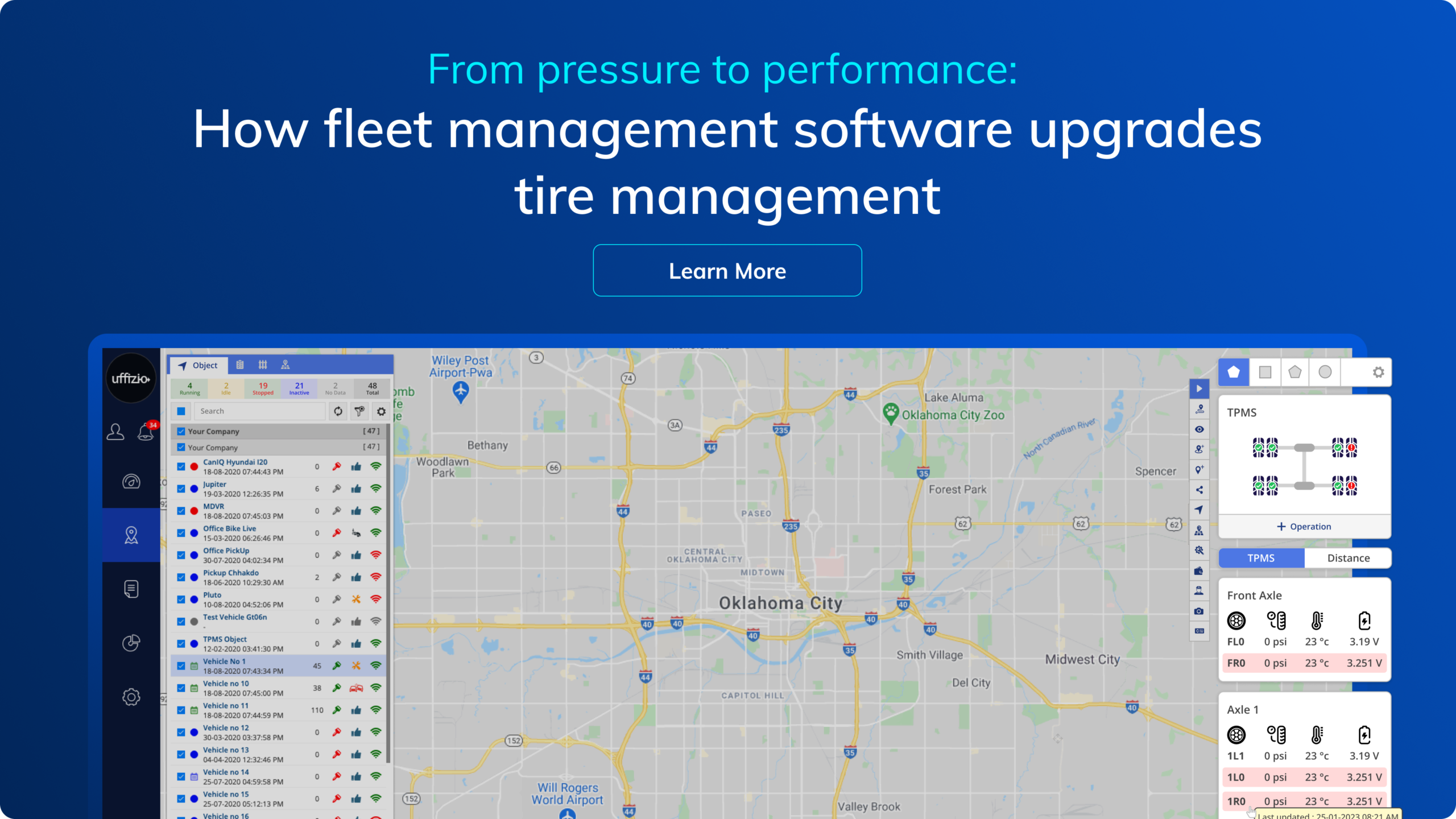
What is a Tire Pressure Sensor? Understanding Its Importance and Benefits

Imagine running a fleet of vehicles where safety and efficiency are top priorities. Now, consider how something as simple as tire pressure can impact both. Tire pressure sensors are a game-changer in this regard. Providing critical data that can prevent accidents, it also reduce fuel costs, and extends tire life. But what exactly are these sensors? Why are they essential for every vehicle in your fleet? In this blog, we’ll break down the importance of tire pressure sensors, how they work, and the benefits they bring to the table. Let’s explore how these devices can be a valuable asset for your business, ensuring both safety and cost-effectiveness in your operations.
What is a Tire Pressure Sensor?
A tire pressure sensor is a small electronic device fitted inside each tire of a vehicle. It continuously monitors the air pressure in the tires and sends this information to the vehicle’s onboard computer. The system promptly notifies the driver whenever the tire pressure deviates from the recommended range, whether it falls below or exceeds it.
Types of Tire Pressure Sensors
Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS):
Installation and Measurement: Direct TPMS sensors are installed inside the tires, typically mounted on the rim. They directly measure the air pressure in the tire using a pressure sensor. This direct measurement ensures accurate and real-time data on the tire’s air pressure.
Real-time Data: These sensors provide real-time data to the driver via the vehicle’s dashboard. The driver can monitor the current tire pressure and receive instant alerts if the pressure becomes too low or too high.
Accuracy: Direct TPMS is more accurate compared to indirect systems because they measure the actual pressure inside the tire. This accuracy helps in maintaining the correct tire pressure, ensuring safety and optimal vehicle performance.
Indirect Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS):
Measurement Method: Indirect TPMS does not measure the tire pressure directly. Instead, it uses the vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) to estimate tire pressure. The system monitors the rotational speed of the tires to detect differences that indicate under-inflation.
Cost and Installation: Indirect TPMS is generally cheaper to install than direct TPMS because it does not require additional sensors inside the tires. It uses existing ABS sensors to estimate the tire pressure.
Accuracy and Limitations: While indirect TPMS is less accurate than direct TPMS, it still provides a reasonable estimation of tire pressure. However, it may not detect slow leaks or small differences in pressure as effectively as direct systems.
How Do Tire Pressure Sensors Work?
Direct TPMS sensors are equipped with a pressure sensor, a temperature sensor, and a radio transmitter. Here’s how they work:
Pressure Measurement:
Function: The sensor measures the air pressure inside the tire. It continuously monitors the pressure and compares it with the recommended pressure levels set by the vehicle manufacturer.
Importance: Proper pressure measurement is crucial for maintaining optimal tire performance. It helps prevent issues like under-inflation, which can lead to tire damage and reduced fuel efficiency.
Temperature Measurement:
Function: The sensor also monitors the tire’s temperature. Temperature changes can affect air pressure, so measuring temperature helps provide more accurate pressure readings.
Importance: By considering the temperature, the sensor can adjust the pressure readings to reflect the actual conditions inside the tire. This adjustment ensures that the driver receives accurate information about the tire pressure.
Data Transmission:
Function: The sensor transmits the data to the vehicle’s onboard computer using a radio signal. This transmission occurs at regular intervals to keep the driver informed about the tire pressure.
Importance: The onboard computer processes the tire pressure data and displays it on the dashboard for the driver to see. If the tire pressure is too low or too high, the system alerts the driver with a warning light or message.
Benefits of Tire Pressure Sensors
Safety:
Risk Reduction: Properly inflated tires reduce the risk of blowouts and accidents. Under-inflated tires can overheat and fail, leading to dangerous blowouts. Over-inflated tires can cause poor handling and increase the risk of a crash.
Handling and Stability: Correct tire pressure ensures better handling and stability. Properly inflated tires maintain their shape and contact with the road, providing better traction and control.
Fuel Efficiency:
Rolling Resistance: Correct tire pressure reduces rolling resistance, leading to better fuel economy. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, causing the engine to work harder and consume more fuel.
Cost Savings: Maintaining proper tire pressure saves money on fuel by improving fuel efficiency. This cost savings adds up over time, especially for vehicles driven frequently.
Tire Longevity:
Even Wear: Properly inflated tires wear out more evenly. Uneven tire wear is a common issue with under-inflated or over-inflated tires, leading to premature tire replacement.
Extended Lifespan: Maintaining the correct tire pressure ensures tires last longer, reducing the need for costly replacements.
Environmental Benefits:
CO2 Emissions: Proper tire pressure reduces CO2 emissions. Under-inflated tires cause higher fuel consumption, leading to increased carbon emissions.
Green Contribution: Maintaining the correct tire pressure contributes to a greener environment by improving fuel efficiency and reducing the carbon footprint of the vehicle.
How to Maintain Tire Pressure Sensors
Regular Checks:
Frequency: Check the tire pressure regularly, even with TPMS. It is advisable to check tire pressure at least once a month and before embarking on long trips.
Tools: Use a reliable tire pressure gauge to ensure accuracy. Digital gauges are more accurate than analog ones and easier to read.
Proper Maintenance:
Cleanliness: Keep the sensors clean and free from dirt. Dirt and debris can interfere with the sensor’s ability to measure pressure accurately.
Careful Handling: Avoid damaging the sensors during tire changes or rotations. Mishandling the sensors can cause them to malfunction or provide inaccurate readings.
Battery Replacement:
Lifespan: Direct TPMS sensors have batteries that need replacement after 5-10 years. The lifespan of the battery depends on the sensor’s usage and environmental conditions.
Replacement: Replace the batteries as recommended by the manufacturer. Some TPMS sensors require professional installation for battery replacement.
Professional Inspections:
Regular Maintenance: Have the sensors inspected by professionals during regular vehicle maintenance. Professional inspections ensure the sensors are functioning correctly and provide accurate readings.
Calibration: Some TPMS sensors may require calibration after installation or tire changes. Professional calibration ensures the sensors provide accurate data.
Common Issues with Tire Pressure Sensors
Sensor Malfunction:
Causes: Sensors can fail due to damage, battery depletion, or manufacturing defects. Physical damage during tire changes or exposure to harsh conditions can cause sensor failure.
Solution: Replace malfunctioning sensors promptly to maintain safety. Regular inspections can identify failing sensors before they cause issues.
False Alarms:
Causes: Sometimes, sensors may trigger false alarms due to temporary pressure changes or sensor malfunctions. Rapid temperature changes or minor pressure fluctuations can cause false alerts.
Solution: Verify the tire pressure manually before taking action. If false alarms persist, have the sensors inspected by a professional.
Interference:
Causes: Radio frequency interference can affect sensor signals. Electronic devices operating on similar frequencies can interfere with the TPMS signal.
Solution: Ensure no electronic devices interfere with the TPMS. If interference is suspected, relocate or turn off the interfering device.
Why Every Vehicle Should Have Tire Pressure Sensors
Mandatory in Many Countries:
Regulations: Many countries have made TPMS mandatory in new vehicles. Regulations require manufacturers to install TPMS in all new cars to ensure safety and compliance.
Safety Assurance: Mandatory TPMS ensures vehicles maintain proper tire pressure, reducing accident risk and enhancing road safety.
Enhanced Driving Experience:
Comfort: Properly inflated tires ensure a smoother and more comfortable ride. Correct tire pressure reduces vibrations and noise, enhancing the driving experience.
Performance: Proper tire pressure improves vehicle handling and braking performance. It ensures optimal contact between the tire and the road, providing better traction and control.
Cost Savings:
Fuel Efficiency: Saves money on fuel, tire replacements, and repairs. Proper tire pressure reduces rolling resistance, leading to lower fuel consumption.
Preventive Maintenance: Prevents costly accidents and breakdowns. Regular tire maintenance, including TPMS, helps avoid unexpected repairs and replacements.
Peace of Mind:
Awareness: Knowing your tires are always at the correct pressure gives peace of mind. TPMS alerts the driver to any pressure issues, ensuring timely action.
Focus: It allows you to focus on the road and enjoy your drive. With TPMS, drivers can concentrate on driving, knowing their tires are in good condition.
Conclusion
Tire pressure sensors are an essential part of modern vehicles, contributing significantly to safety, fuel efficiency, and overall performance. By understanding how they work and maintaining them properly, you can ensure a safer and more economical driving experience. Make sure to regularly check your tire pressure, keep your sensors in good condition, and enjoy the benefits of this smart technology.