Cranes are critical in many industrial sectors, and their operations are inherently risky, requiring precise control. Tilt sensors are a game-changer for enhancing the safety and efficiency of crane operations.
Introduction
Challenges
Safety Risks: Without a tilt sensor, there is an increased risk of the crane operating outside of its safe working angle, leading to potential accidents.
Operational Inefficiency: Lacking data on the boom’s movements, operators might use the crane inefficiently, leading to increased operational times and potential project delays.
Manual Monitoring: Operators need to rely on manual checks or visual assessments to ensure the boom is not exceeding safe angles, which can be less reliable and more time-consuming.
Increased Downtime: Without accurate usage data, preventive maintenance is challenging to schedule, potentially leading to increased downtime and repair costs.
Challenges
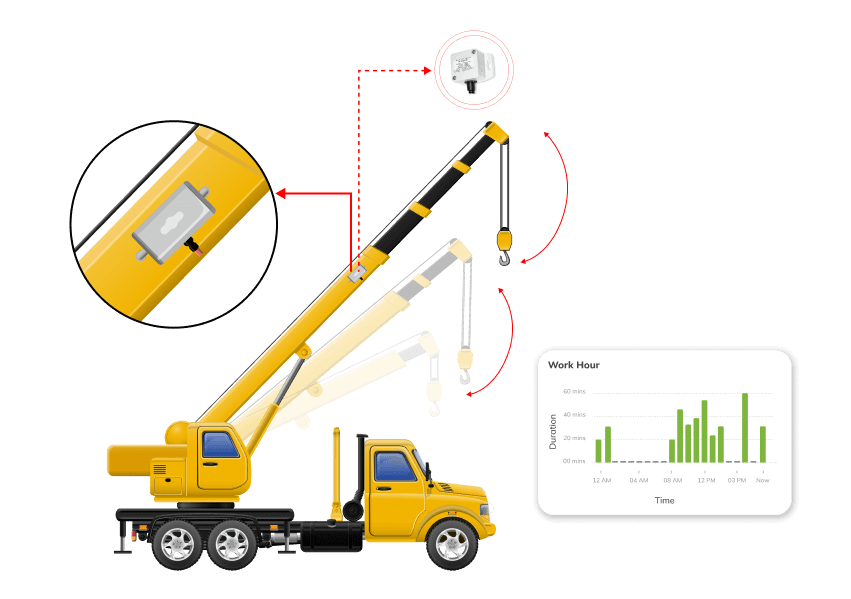
Solution
Real-time Boom Monitoring: Installed on the telescopic boom, the sensor reports every movement, providing data on the boom’s angle, frequency of movements, and the time spent working.
Increased Safety: With the angle data provided by the sensor, operators can ensure the crane operates within its safe working limits, thereby reducing the risk of accidents.
Operational Data: The sensor allows for detailed tracking of the crane’s operations, which can be used to optimize work schedules and improve efficiency.
Maintenance Scheduling: Usage data from the sensor helps schedule maintenance based on the crane’s actual working hours, reducing unexpected breakdowns.
Challenges
Results
Enhanced Safety: Significant reduction in the incidence of accidents due to over-tilting.
Operational Efficiency: Reduced downtime through proactive monitoring, leading to more efficient project timelines.
Regulatory Compliance: Assurance of adherence to safety regulations, avoiding fines and work stoppages.
Mitigation of Environmental Risks: Better preparedness for environmental factors affecting crane stability.


